A decade ago, brands optimized for Google.
Today, they’re learning to optimize for ChatGPT, Gemini, and the next generation of AI-powered assistants that summarize the internet in seconds.
The rules of discovery are changing.
Instead of scrolling through blue links, users increasingly ask AI models direct questions, and trust the answers. That means your website may soon be discovered by a model, not just a person.
For businesses, this shift brings both risk and opportunity: risk if your site can’t be accurately understood by AI, and opportunity if it can.
Why “AI Visibility” Is the New SEO
When you ask ChatGPT, “What’s the best small business accounting software,” or “How do I start a coffee shop,” the response doesn’t just pull from memory; it’s synthesized from patterns in web data.
That means the model must first understand your content.
If your website’s structure, semantics, or copy are confusing, the AI can’t summarize it correctly, and your brand gets left out of the answer.
This is the next phase of digital optimization: not just ranking higher, but being interpreted accurately.
It’s no longer about visibility in a search engine; it’s about comprehensibility in a reasoning engine.
How AI Reads Your Website
AI models don’t “crawl” your site like search bots. They rely on structured data, markup, and contextual clarity to infer meaning.
The easier your content is to parse, the more likely it is to appear in AI-generated recommendations or summaries.
Here’s what they pay attention to:
- Clear hierarchy: Headings (H1–H3) that describe intent, not fluff.
- Semantic HTML: Proper tags for navigation, articles, and sections.
- Contextual copy: Plain, descriptive language over buzzwords.
- Structured data: Schema markup that defines your business, services, and credibility signals.
- Link context: Internal and external links that support meaning, not keyword stuffing.
When this foundation is strong, AI systems can confidently connect your content to user intent and reference it as a trustworthy source.
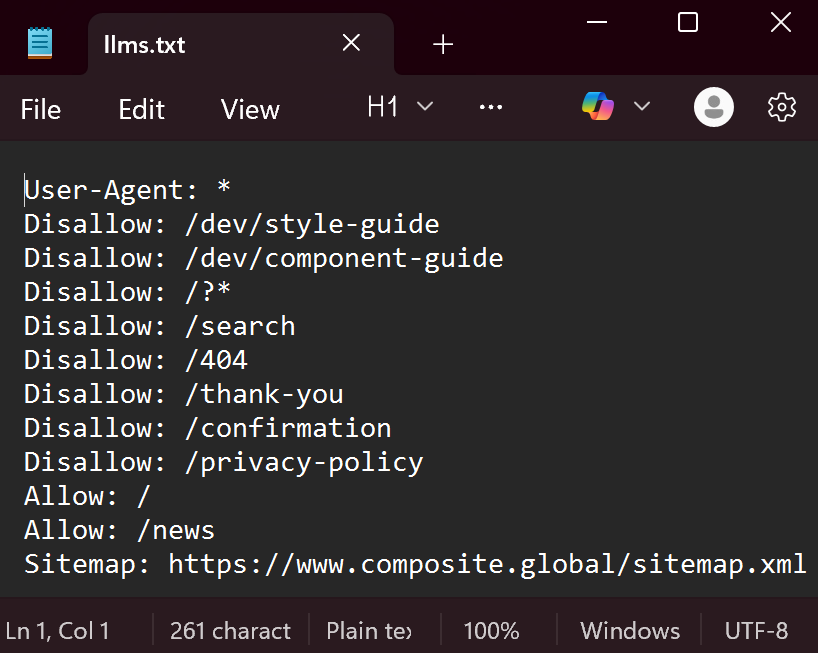
Introducing llms.txt: A New Way to Communicate with AI Models
Just as robots.txt tells search engines which pages to crawl, a new emerging file, llms.txt, aims to tell AI models how to interact with your content.
Still experimental, llms.txt allows site owners to specify:
- Which models can access or train on your site’s data.
- Which directories or file types are restricted.
- Whether commercial reuse of your content is permitted.
In short, it helps brands control how their content enters the AI ecosystem.
You can think of it as AI consent management for your website.
As explored in Composite’s detailed guide to llms.txt and AI SEO, adopting this file early sends a clear signal: your site is AI-ready, compliant, and open to responsible indexing.
For a detailed guide on generating and implementing llms.txt files in webflow, read SEO for ChatGPT: Help LLMs Understand Your Website.
Clarity Is Machine Logic
For AI, clarity equals credibility.
The more clearly you communicate your meaning, the more confidently a model can summarize or cite you.
That means trimming jargon, simplifying structure, and writing in full, self-contained sentences that make sense even out of context.
Compare these two examples:
- “We revolutionize client engagement through next-gen digital frameworks.”
- “We help companies design and develop websites that attract more clients through better user experience.”
The second version is easier for both humans and machines to interpret. It uses verbs and nouns that describe action and result. It’s the language of logic, not marketing hype.
Schema Markup: The Bridge Between Your Words and AI’s Understanding
Schema markup, the structured data embedded in your site’s code, is becoming the bridge between your content and AI reasoning.
When you define entities like Organization, Product, or FAQ, you’re teaching machines what each section means.
That helps models connect your site to relevant queries with more accuracy.
For example, a local business might use:
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “LocalBusiness”,
“name”: “Smith & Co Financial Advisors”,
“address”: “123 Main Street, Denver, CO”,
“serviceArea”: “Colorado”,
“url”: “https://smithcofinance.com”
}
That structured clarity ensures AI knows exactly who you are, what you offer, and where you serve customers, which will increasingly feed directly into AI-generated recommendations.
Content That Explains Itself
In the AI-driven internet, content has to “stand alone.”
When a model extracts a paragraph from your site, it may appear detached from its original context.
That’s why each section should be written as a complete thought.
Think less like a novelist and more like a teacher who knows their lessons might be quoted out of order.
Strong explanatory copy increases your odds of accurate citation and reduces the risk of misinterpretation when AI summarizes your work.
Earning AI Trust Through Consistency
AI models weigh signals of authority much like search engines do: consistency, reliability, and reputation matter.
They draw on multiple data sources: your website, mentions across the web, and structured profiles like LinkedIn or Crunchbase.
Maintaining consistency across all of them builds a clearer knowledge graph of your brand.
When your company’s name, description, and offerings are uniform everywhere, you create what Google calls “entity clarity,” the foundation for trustworthy AI understanding.
Consistency doesn’t just help ranking; it helps reasoning.
Designing for AI Readability
Even layout influences AI interpretation.
A site that’s chaotic, with text hidden in sliders or images, can confuse both users and language models.
Simple design principles improve AI readability:
- Use live text instead of text baked into images.
- Keep navigation semantic (<nav>, <main>, <footer>).
- Ensure page speed and accessibility scores remain high.
- Use descriptive image alt text and know that models read it too.
Accessibility and AI optimization often go hand-in-hand.
A site that’s clear to a screen reader is clear to a crawler and clear to an AI trying to summarize meaning.
AI Summaries Will Replace Search Snippets
Soon, when users search for information, they may not see a list of websites at all, just a single AI-generated summary.
The sources that models trust most will be referenced or linked directly in that output.
That’s the next wave of digital competition: brands aren’t just fighting for the top search position; they’re fighting for inclusion in AI discourse.
To prepare:
- Strengthen structured data.
- Simplify and clarify copy.
- Add an llms.txt file for transparency.
- Maintain consistent information across every channel.
These steps ensure your brand isn’t just visible, but understood.
What AI-Ready Businesses Will Look Like
Within a few years, most forward-thinking companies will treat AI optimization the same way they treat SEO today.
Marketing teams will regularly audit websites for both human readability and machine clarity.
An AI-ready business will:
- Write content that explains concepts, not just promotes products.
- Tag and structure information for algorithmic interpretation.
- Use transparent AI policies to signal credibility and consent.
- Collaborate across design, development, and SEO teams under one unified goal: clarity.
The companies that adapt early will dominate AI-driven discovery, not because they have more data, but because they’re easier to understand.
The Future: From Search Engines to Understanding Engines
Search was built to find answers. AI is built to generate them.
That’s a profound shift. It means your brand’s visibility depends not on how often you publish, but on how clearly you communicate.
As AI systems take over more of the discovery experience, clarity becomes the ultimate marketing strategy that serves both users and machines.
Businesses that recognize this early will lead the next era of digital visibility:
- Trusted not just by customers, but by the algorithms they rely on.
- Credible not just in content, but in structure.
- Findable not by keyword, but by comprehension.
That’s the true future of optimization—designing for understanding.
